
🔑 Key management
Generate new session keys
In Substrate, session keys are cryptographic keys used by validators for various consensus-related tasks, such as finalization and block production. Each validator uses a set of session keys, which are periodically rotated for enhanced security. Here’s how to generate new session keys:
curl -s -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"id":1, "jsonrpc":"2.0", "method": "author_rotateKeys", "params":[]}' http://localhost:9944
Example output:
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"result":"0x64ce7ca011d983115c7e8e94a8cb3843b78c3d3a5b8f3f1c32bb75afac499f6aecae63af27f524a3caffa869295519abcddaa372982ad644d4000daa7dc2c1d4f0553848661e55d645aa00758994c4fcec63a98700aa6c88c859d64d47363150e03b88a067e60cc0ba7333a88db5bf44ca6fa5e3327c64c5ec02244b168fe803",
"id":1
}
Session keys are generated and stored in .avail/data/chains/avail_da_mainnet/keystore folder.
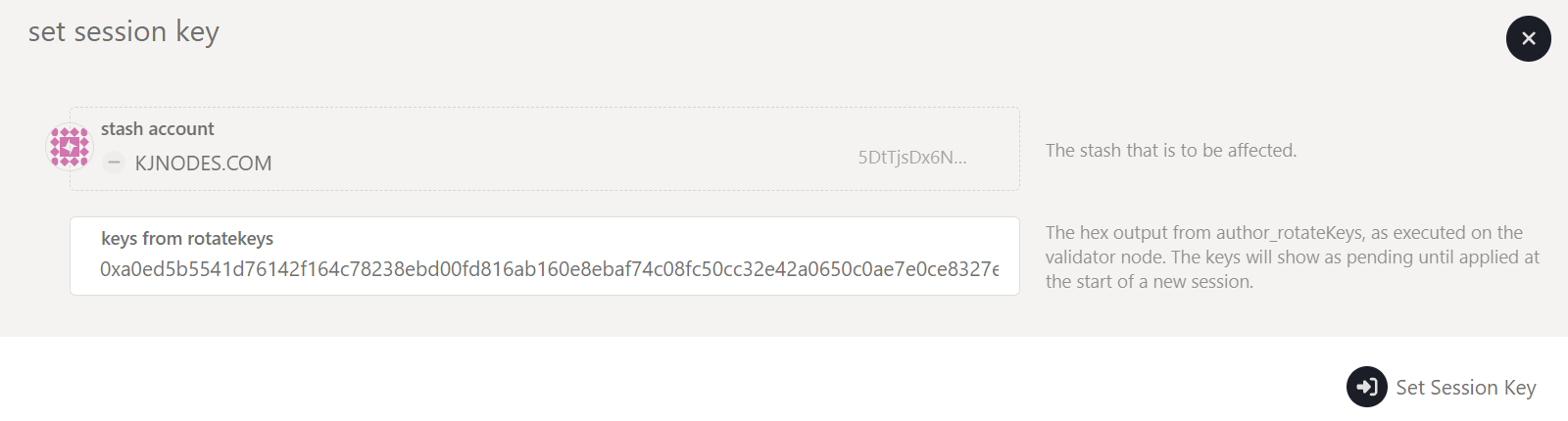
Submit Session Keys
You must inform the network of your Session Keys by signing and submitting the setKeys extrinsic. This action associates your validator with your Controller account.
- Navigate back to the
Stakingtab. - Click on
Set Session Keyand enter the hex-encoded result. - Click
Set Session Keyand enter your password when prompted.
🚨 Maintenance
Get node binary version
Returns the version of the node software.
curl -s -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"id":1, "jsonrpc":"2.0", "method": "system_version", "params":[]}' http://localhost:9944 | jq .result
Example output:
"2.2.0-a6600ea38c9"
Check your node health
Provides health information about the node, including whether it is syncing and the number of connected peers.
curl -s -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"id":1, "jsonrpc":"2.0", "method": "system_health", "params":[]}' http://localhost:9944 | jq .result
Example output:
{
"peers": 37,
"isSyncing": false,
"shouldHavePeers": true
}
If isSyncing is false, it means your node is fully caught up with the latest block
Show local peer identity
Returns the local peer ID of the node.
curl -s -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"id":1, "jsonrpc":"2.0", "method": "system_localPeerId", "params":[]}' http://localhost:9944 | jq .result
Example output:
"12D3KooWJy5FcyhmCRFSmaWnXhkfAXPffTeYAtppfmZN2FqEGPBv"
Show node type
Returns the roles the node is performing (e.g., full, authority).
curl -s -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"id":1, "jsonrpc":"2.0", "method": "system_nodeRoles", "params":[]}' http://localhost:9944 | jq .result[0]
Example output:
"Authority"
Show connected peer list
Returns a list of connected peers and their information.
curl -s -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"id":1, "jsonrpc":"2.0", "method": "system_peers", "params":[]}' http://localhost:9944 | jq .result
Example output:
[
{
"peerId": "12D3KooWK85zotBy9jjgVhHzsvntAWWzRxTosF3RxwnJ9zJsGQbi",
"roles": "FULL",
"bestHash": "0xaae047fd9e5255d7c8149866c83da7eb85af70c4dcc1c49951e6dcc7289badf7",
"bestNumber": 499060
},
{
"peerId": "12D3KooWBXk3rcfKkvd1YbJ8fHPH4WZy34QCw8Czrvqf6cbmrdKh",
"roles": "FULL",
"bestHash": "0xaae047fd9e5255d7c8149866c83da7eb85af70c4dcc1c49951e6dcc7289badf7",
"bestNumber": 499060
},
{
"peerId": "12D3KooWLVJtN3hpUJYPjQzGKiHnbw6fpD5vvH5EkztdP1VAAgrj",
"roles": "FULL",
"bestHash": "0xaae047fd9e5255d7c8149866c83da7eb85af70c4dcc1c49951e6dcc7289badf7",
"bestNumber": 499060
},
{
"peerId": "12D3KooWFB6wBdwS1aacu3QZdmZb2sPDiVxP9iLFecLBiHKZELCX",
"roles": "FULL",
"bestHash": "0xaae047fd9e5255d7c8149866c83da7eb85af70c4dcc1c49951e6dcc7289badf7",
"bestNumber": 499060
}
]
Get block sync info
Returns the synchronization state of the node, including information about the starting block, the current block, and the highest block known to the node.
curl -s -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"id":1, "jsonrpc":"2.0", "method": "system_syncState", "params":[]}' http://localhost:9944 | jq .result
Example output:
{
"startingBlock": 0,
"currentBlock": 29382,
"highestBlock": 499081
}
Get the list of supported methods
curl -s -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"rpc_methods","params":[],"id":1}' http://localhost:9944 | jq .result
Example output:
{
"methods": [
"account_nextIndex",
"author_hasKey",
"author_hasSessionKeys",
"author_insertKey",
"author_pendingExtrinsics",
"author_removeExtrinsic",
"author_rotateKeys",
"author_submitAndWatchExtrinsic",
"author_submitExtrinsic",
"author_unwatchExtrinsic",
"babe_epochAuthorship",
"chainHead_unstable_body",
"chainHead_unstable_call",
"chainHead_unstable_continue",
"chainHead_unstable_follow",
"chainHead_unstable_header",
"chainHead_unstable_stopOperation",
"chainHead_unstable_storage",
"chainHead_unstable_unfollow",
"chainHead_unstable_unpin",
"chainSpec_v1_chainName",
"chainSpec_v1_genesisHash",
"chainSpec_v1_properties",
"chain_getBlock",
"chain_getBlockHash",
"chain_getFinalisedHead",
"chain_getFinalizedHead",
"chain_getHead",
"chain_getHeader",
"chain_getRuntimeVersion",
"chain_subscribeAllHeads",
"chain_subscribeFinalisedHeads",
"chain_subscribeFinalizedHeads",
"chain_subscribeNewHead",
"chain_subscribeNewHeads",
"chain_subscribeRuntimeVersion",
"chain_unsubscribeAllHeads",
"chain_unsubscribeFinalisedHeads",
"chain_unsubscribeFinalizedHeads",
"chain_unsubscribeNewHead",
"chain_unsubscribeNewHeads",
"chain_unsubscribeRuntimeVersion",
"childstate_getKeys",
"childstate_getKeysPaged",
"childstate_getKeysPagedAt",
"childstate_getStorage",
"childstate_getStorageEntries",
"childstate_getStorageHash",
"childstate_getStorageSize",
"grandpa_proveFinality",
"grandpa_roundState",
"grandpa_subscribeJustifications",
"grandpa_unsubscribeJustifications",
"mmr_generateProof",
"mmr_root",
"mmr_verifyProof",
"mmr_verifyProofStateless",
"offchain_localStorageGet",
"offchain_localStorageSet",
"payment_queryFeeDetails",
"payment_queryInfo",
"rpc_methods",
"state_call",
"state_callAt",
"state_getChildReadProof",
"state_getKeys",
"state_getKeysPaged",
"state_getKeysPagedAt",
"state_getMetadata",
"state_getPairs",
"state_getReadProof",
"state_getRuntimeVersion",
"state_getStorage",
"state_getStorageAt",
"state_getStorageHash",
"state_getStorageHashAt",
"state_getStorageSize",
"state_getStorageSizeAt",
"state_queryStorage",
"state_queryStorageAt",
"state_subscribeRuntimeVersion",
"state_subscribeStorage",
"state_traceBlock",
"state_trieMigrationStatus",
"state_unsubscribeRuntimeVersion",
"state_unsubscribeStorage",
"subscribe_newHead",
"sync_state_genSyncSpec",
"system_accountNextIndex",
"system_addLogFilter",
"system_addReservedPeer",
"system_chain",
"system_chainType",
"system_dryRun",
"system_dryRunAt",
"system_health",
"system_localListenAddresses",
"system_localPeerId",
"system_name",
"system_nodeRoles",
"system_peers",
"system_properties",
"system_removeReservedPeer",
"system_reservedPeers",
"system_resetLogFilter",
"system_syncState",
"system_unstable_networkState",
"system_version",
"transactionWatch_unstable_submitAndWatch",
"transactionWatch_unstable_unwatch",
"unsubscribe_newHead"
]
}
Reset the node data
Before purging, ensure you back up any important data, like keys or configuration files. Be aware that purging data means your node will need to resynchronize with the network, which can take some time depending on the network and your internet speed.
avail-node purge-chain --chain mainnet --base-path $HOME/.avail/data
sudo systemctl restart avail.service
Remove node
Warning! All chain data will be lost! Make sure you back up any important data, like keys or configuration files!
cd $HOME
sudo systemctl stop avail.service
sudo systemctl disable avail.service
sudo rm /etc/systemd/system/avail.service
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
rm -f $(which avail-node)
rm -rf $HOME/.avail
⚙️ Service Management
Reload service configuration
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Enable service
sudo systemctl enable avail.service
Disable service
sudo systemctl disable avail.service
Start service
sudo systemctl start avail.service
Stop service
sudo systemctl stop avail.service
Restart service
sudo systemctl restart avail.service
Check service status
sudo systemctl status avail.service
Check service logs
journalctl -u avail.service -f --no-hostname -o cat